Medicare Advantage
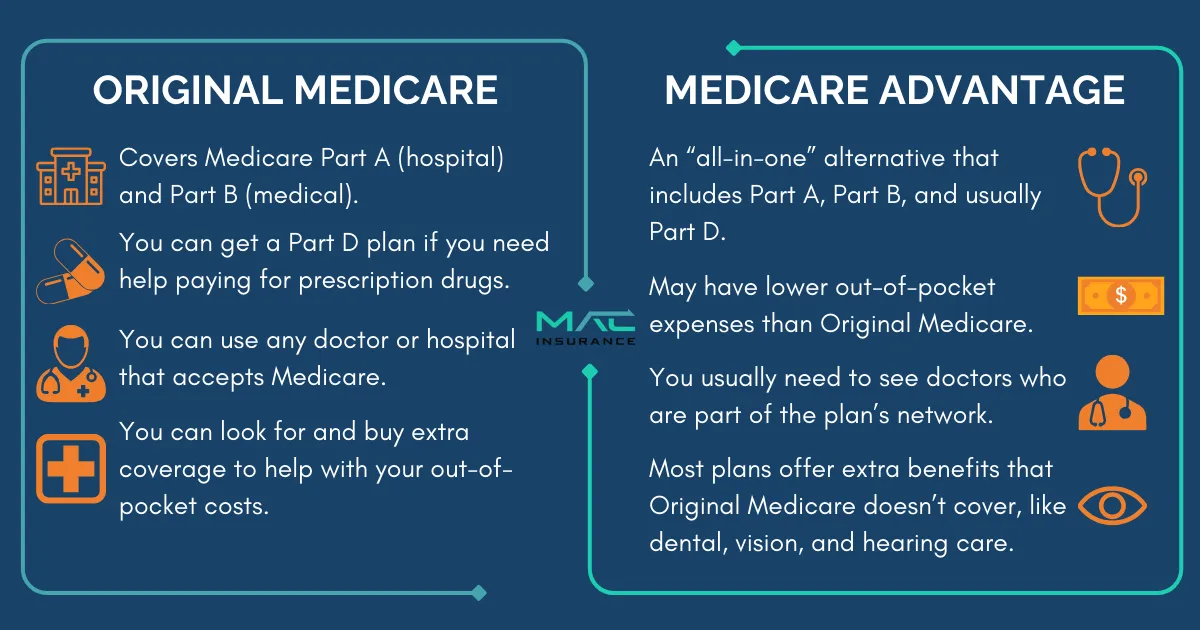
Medicare Advantage (Part C) is a private insurance alternative to Original Medicare (Parts A and B). These plans, offered by private insurers, combine hospital (Part A) and medical (Part B) coverage into one plan. Many also include extra benefits like vision, dental, and prescription drug coverage.
Medicare Advantage (Part C) Eligibility and Enrollment
Who Can Enroll?
You can join a Medicare Advantage plan if you:
● Are enrolled in Medicare Part A (Hospital Insurance) and Part B (Medical Insurance).
● Live in the plan’s service area.
When Can You Enroll?
● Initial Enrollment Period (IEP): A 7-month window around your 65th birthday.
● Annual Enrollment Period (AEP): October 15 – December 7 (coverage starts January 1).
● Medicare Advantage Open Enrollment (OEPMA): January 1 – March 31 (switch plans or return to Original Medicare).
● Special Enrollment Periods (SEPs): Available for specific life events like moving or losing other coverage.
Special Considerations
● Dual Eligibility: If you qualify for both Medicare and Medicaid, you may be eligible for Special Needs Plans (SNPs).
● End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD): Since 2021, ESRD patients can enroll in Medicare Advantage.
● SNPs: Tailored plans for those with chronic conditions or special care needs.
Choosing the Right Plan
● Coverage & Benefits: Look for extras like dental, vision, and wellness programs.
● Provider Network: Check if your doctors and hospitals are included.
● Costs: Compare premiums, copays, and out-of-pocket expenses.
This guide helps you understand Medicare Advantage enrollment and find the best plan for your needs.
Medicare Advantage Enrollment Periods

Knowing when to enroll in a Medicare Advantage plan is important.
Here are the key enrollment periods:
Initial Enrollment Period (IEP)
A 7-month window around your 65th birthday (3 months before and after).
● Turning 65? You can enroll in Medicare Advantage.
● Under 65 with a disability? You’re eligible after receiving Social Security disability benefits for 24 months.
Special Enrollment Period (SEP)
Certain life events allow you to enroll or change plans anytime:
● Moving out of your plan’s service area.
● Qualifying for extra financial help.
● Entering a nursing home.
General Enrollment Period (GEP)
● You can sign up from January 1 to March 31 each year — this is called the General Enrollment Period.
● Your coverage starts the month after you sign up.
● If you don’t qualify for a Special Enrollment Period, you might have to pay a monthly late enrollment penalty.
Annual Enrollment Period (AEP) – Oct 15 to Dec 7
● Join, switch, or drop a Medicare Advantage plan.
● Changes take effect on January 1.
Medicare Advantage Open Enrollment Period (MAOEP) – Jan 1 to Mar 31
● If you already have a Medicare Advantage plan, you can switch plans or return to Original Medicare.
● Changes take effect the next month.
Understanding these timeframes helps you avoid coverage gaps and make informed decisions.
Medicare Advantage Coverage: What’s Included?
Medicare Advantage (Part C) covers everything Original Medicare (Parts A & B) does—and often more.
Inpatient Care (Hospital Coverage)
Covers services typically under Medicare Part A, including:
● Hospital stays
● Skilled nursing facility care
● Home health care
Note: Hospice care is still covered by Original Medicare.
Outpatient Care (Medical Coverage)
● Includes services under Medicare Part B, such as:
● Doctor visits (primary care & specialists)
● Lab tests, X-rays, and diagnostic screenings
● Mental health care (inpatient & outpatient)
● Ambulance services
● Physical, occupational, and speech therapy
● Vaccinations
● Medical equipment (wheelchairs, walkers, etc.)
Extra Benefits Medicare Advantage May Offer
Many plans include additional perks not covered by Original Medicare:
● Dental, vision, and hearing services
● Fitness programs (like SilverSneakers)
● Travel coverage for emergencies outside the U.S.
● Allowance for over-the-counter health products
Since benefits vary by plan, always review the details to find the right coverage for your needs.

Medicare Advantage Costs: What to Expect
Medicare Advantage plan costs vary widely—from $0 premium plans to those costing several hundred dollars per month. While $0 premium plans are common, higher-cost plans often include more benefits, broader provider networks, and lower out-of-pocket expenses.
Key Cost Factors:
Premiums
● Some plans have $0 monthly premiums.
● You must still pay the Medicare Part B premium.
Deductibles
● Some plans have separate deductibles for medical services and prescriptions.
● A few $0 premium plans also have $0 deductibles.
Copayments & Coinsurance
● Copayments = Fixed fees for doctor visits or prescriptions.
● Coinsurance = A percentage of costs you pay after meeting your deductible.
Plan Type
● Costs vary based on the plan type (HMO, PPO, PFFS), affecting premiums and provider flexibility.
Out-of-Pocket Maximum
● Medicare Advantage plans cap your total yearly expenses, protecting you from high medical bills.
Location & Travel
● Some plans are region-specific, so frequent travelers may need a plan with better out-of-network coverage.
Income-Based Costs
● Higher-income individuals may pay more due to IRMAA (Income-Related Monthly Adjustment Amounts).
Choosing the Right Plan
Compare plans carefully to find one that fits your budget and healthcare needs.
Choosing the Right Medicare Advantage Plan
Medicare Advantage plans come in different types, each with unique features:
● HMO (Health Maintenance Organization) – Lower costs, but you must use network doctors and get referrals for specialists.
● PPO (Preferred Provider Organization) – More flexibility to see out-of-network doctors, but at a higher cost.
● PFFS (Private Fee-for-Service) – Freedom to see any doctor who accepts the plan’s terms, but provider acceptance may vary.
● SNP (Special Needs Plan) – Designed for people with specific health conditions or financial needs.
● MSA (Medical Savings Account) – Combines a high-deductible health plan with a medical savings account to help cover costs.
Each plan type has pros and cons, so it's important to choose one that fits your healthcare needs and budget.
For a more detailed explanation, consider exploring Medical Savings Account plans.
Health Maintenance Organization (HMO) Plans
Who Can Enroll?
● You must have Original Medicare (Parts A & B) and live in an area where an HMO plan is offered.
What’s Covered?
● All hospital and medical services covered by Original Medicare
● Many plans include prescription drug coverage (Part D)
● Extra benefits like dental, vision, hearing, fitness programs, or meal delivery
How HMO Plans Work
● You must use in-network doctors and hospitals for coverage
● Seeing out-of-network providers usually means paying the full cost
Costs
● Premiums: Some plans are $0, others charge a monthly fee
● Deductibles: Some plans have no deductible
● Copayments: Typically $0–$50 per visit, depending on the provider
● Coinsurance: You may pay 20% after meeting your deductible
Why Choose an HMO?
● One Plan for Everything – Combines hospital, medical, and often drug coverage
● Cost Protection – Out-of-pocket limits help prevent high medical bills
Medicare Advantage HMO plans are a great choice if you want lower costs, extra benefits, and coordinated care.
Preferred Provider Organization (PPO) Plans
Why Choose a PPO Plan?
● More Freedom – See any doctor or specialist without a referral
● In-Network & Out-of-Network Coverage – Lower costs in-network, but you can still see out-of-network providers
Costs to Consider
● Premiums – Some plans have a monthly cost (separate from your Part B premium)
● Deductibles – There may be separate deductibles for medical services and prescription drugs
● Copayments – Costs vary based on whether the provider is in-network or out-of-network
● Out-of-Pocket Maximum – You’ll have separate limits for in-network and out-of-network expenses
PPO plans are ideal if you want flexible coverage, a wider choice of doctors, and no specialist referrals.
Private Fee-for-Service (PFFS) Plans
How It Works:
● Use In-Network Providers – Lower costs with contracted providers
● Out-of-Network Costs – Higher fees or no coverage for non-emergency care
● Prescription Drug Coverage – Some plans include it
Key Benefits:
● No Primary Care Doctor Required
● No Specialist Referrals Needed
PFFS plans offer more flexibility but may have higher costs if you go outside the network. Always check provider acceptance before getting care.
Special Needs (SNP) Plans
Who Qualifies?
● People in nursing homes or needing at-home nursing care
● Those eligible for both Medicare & Medicaid
● Individuals with certain chronic or disabling conditions
Key Benefits:
● Includes Medicare Part D drug coverage
● Access to specialist doctors for your condition
● Requires a primary care doctor and usually referrals
If you meet the eligibility requirements for an SNP, you can enroll at any time.
Medicare Advantage and TRICARE
Who is Eligible?
● Military personnel (active/retired), spouses, and dependents with TRICARE
● Age 65+ and eligible for Medicare
How It Works:
● Medicare Advantage (Part C) becomes your primary insurance
● TRICARE serves as secondary coverage
● You must use your Medicare Advantage plan’s network providers
Important Note:
🚨 Medicare Advantage plans don’t automatically coordinate with TRICARE—you may need to file a secondary claim with TRICARE yourself.
For further assistance with Medicare Advantage, feel free to consult with one of our Medicare agents or consultants.
Ask us about benefits in your area.
Call us today!
Medicare Advantage
How to Enroll in
MEDICARE ADVANTAGE
Once you've applied for Medicare Parts A and B, it's important to consult with a licensed agent to determine if a Medicare Advantage plan is the right fit for you. We'll go over the benefits and drawbacks of these plans to ensure you fully understand your choices.
If you decide to enroll in a Part C plan, we'll explore various options and providers to secure the best coverage at a competitive rate. We'll handle the application process for you and remain available to answer any questions once your coverage starts.
ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS TO BE ADVISED ON:

What does Medicare Advantage cover that Original Medicare doesn’t?
Medicare Advantage may cover extra benefits that Original Medicare doesn’t, such as dental, vision, hearing, prescription drugs, fitness programs, and transportation services. Coverage varies by plan.
How is Medicare Advantage (Part C) funded?
Some Part C plans have a $0 premium, so people often ask how they are funded. The government pays private insurance companies to provide these plans and cover medical costs. Instead of Medicare paying the bills, the insurance company does. Some plans may also have premiums, copays, and coinsurance.
Is Medicare Advantage the same as a Medicare Supplement plan?
No, Medicare Supplement plans work with Original Medicare to help cover costs. Medicare Advantage plans replace Original Medicare and work separately.
Does Medicare Advantage cover emergency and urgent care?
Yes, Medicare Advantage covers emergency and urgent care anywhere in the U.S., even outside the plan’s network. Some plans may also cover emergency care abroad.
Why should I consider a Medicare Advantage plan?
Medicare Part C is optional, but enrolling in a Medicare Advantage plan or a Medigap policy can help cover costs that Original Medicare doesn’t pay for.
📩 Contact us today and let us represent you for FREE!
We are not connected with or endorsed by the United States government or the federal Medicare program. We do not offer every plan available in your area, and any information we provide is limited to those plans we do offer in your area. Please get in touch with Medicare.gov or 1-800-MEDICARE to get information on all your options.
Copyright © 2025 MAC Insurance. All rights reserved.








